When collaborating with GitHub, we often use private hosts for CI/CD tasks.
GitHub provides documentation to guide users through the initial installation steps, and following the steps will successfully configure the setup.
Problem Description
However, your host will often need to reboot. If no configuration is set up, the Runner service will fall asleep indefinitely. This issue can be forgotten until someone notices there’s no response or receives a complaint, which may have already been days later.
This kind of problem can happen repeatedly and become very annoying!
Therefore, we need to make it run automatically!
Configuration Process
To automatically run a task after the host boots, we can use systemd.
-
Create a new systemd service file:
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/actions-runner.service -
Paste the following content into the file:
/etc/systemd/system/actions-runner.service[Unit]
Description=GitHub Action Runner
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=your-username
WorkingDirectory=/home/your-username/actions-runner
ExecStart=/home/your-username/actions-runner/run.sh
Restart=always
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetPay attention to the highlighted areas:
User,ExecStart, andWorkingDirectoryshould be changed to your own username.
-
Tell systemd to reload the new service configuration:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload -
Enable the service so it starts automatically when the host boots:
sudo systemctl enable actions-runner.service -
Now you can manually start the service or reboot to test it:
sudo systemctl start actions-runner.service
With this method, the actions-runner will automatically run in the background when your host boots.
If you want to stop the service, you can use the following command:
sudo systemctl stop actions-runner.service
Make sure that run.sh has executable permissions.
Check the Status
When managing a service with systemd, you can check the logs to understand its current status.
Use the following command:
sudo journalctl -u actions-runner.service -f
Explanation of the parameters:
-u actions-runner.service: Only show logs for the service named actions-runner.-f: This option makes journalctl follow the latest logs, so you can see the new output in real time.
Additionally, if you want to check the current status of the service, you can use:
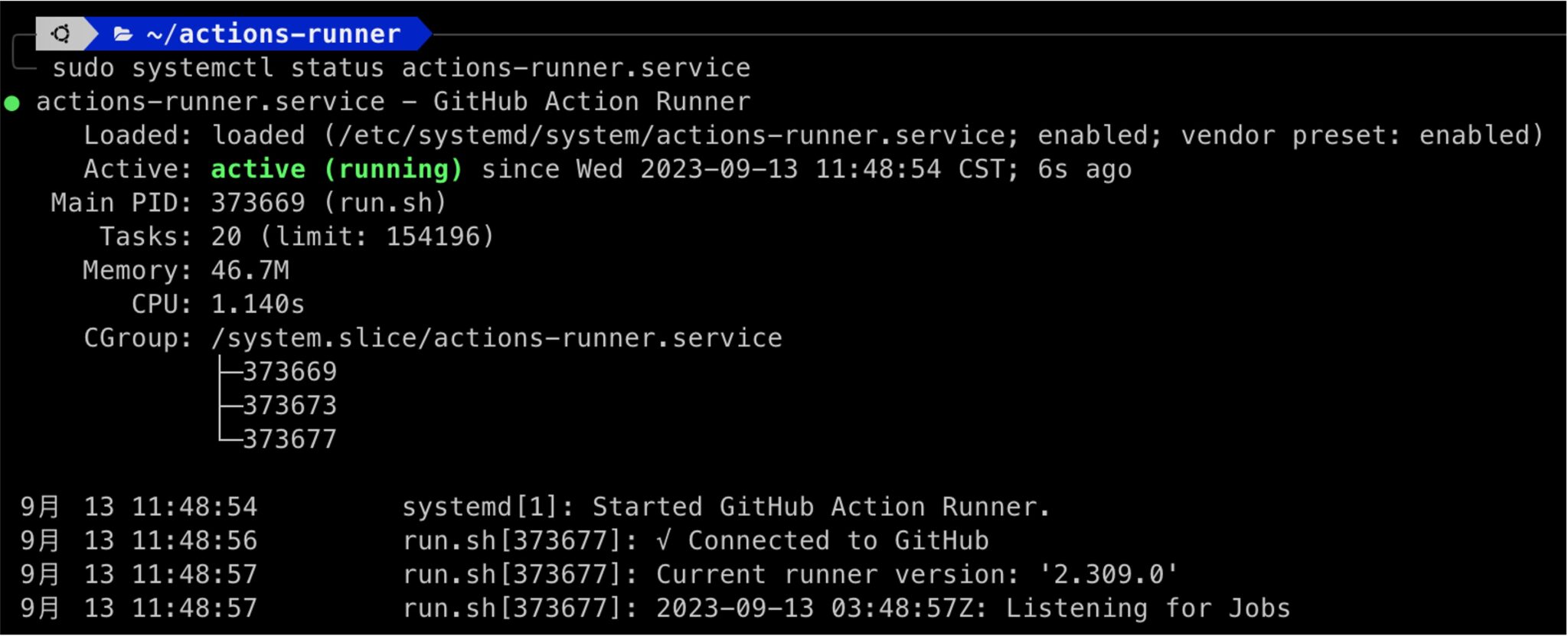
sudo systemctl status actions-runner.service
This will display the current status of the actions-runner service, including whether it's running and the most recent log output:
Reconfigure
This part is off-topic and unrelated to auto-running.
If the original Runner is missing (usually due to switching a repository between Public and Private), or the Runner hasn’t been invoked in a long time and got lost!
In this case, you’ll need to reconfigure:
-
Obtain a new Token from your GitHub account.
-
Go to your actions-runner folder (or another folder you named) and delete the
.runnerfile, then run the configuration command:./config.sh --url ... (use the new Token configuration)
The other steps are the same, and after configuring, just restart the service. Your support keeps my AI & full-stack guides coming. From idea to launch—efficient systems that are future-ready. Need a tech partner or custom solution? Let's connect.☕ Fuel my writing with a coffee
AI / Full-Stack / Custom — All In
All-In Bundle
🚀 Ready for your next project?

